Division of Coronary Diseases
More details
Acute Myocardial Infarction
What is acute myocardial infarction?
Acute myocardial infarction is a condition where a coronary artery that delivers blood to heart muscle is suddenly clogged, causing a shortage in oxygen and nutrients. The main underlying cause of acute myocardial infarction is atherosclerosis. A distinct difference between acute myocardial infarction and angina pectoris is that in acute myocardial infarction, the loss of blood supply leads to cardiac muscle death (necrosis). This mechanism of injury is similar to that of acute cerebral infarction and other ischemic disorders. Acute myocardial infarction is a life-threatening condition. If this condition is not addressed immediately, it may cause irreversible damage. Patients that survive may experience recurrent episodes of heart failure and arrhythmia. For these reasons, NCVC Hospital has a multidisciplinary team of experts engaged in emergency and acute intensive care to seek optimal outcomes through rapid recanalization, reperfusion, and other measures.
Acute Myocardial Infarction Care at the NCVC Hospital's CCU
In order to provide superacute management of myocardial infarction, the NCVC Hospital's Coronary Care Unit (CCU) was established 30 years ago. This is one of the longest-standing CCUs in Japan with an accumulated wealth of experience and expertise. The figure below illustrates improvements over time in clinical outcomes in the NCVC Hospital's CCU.
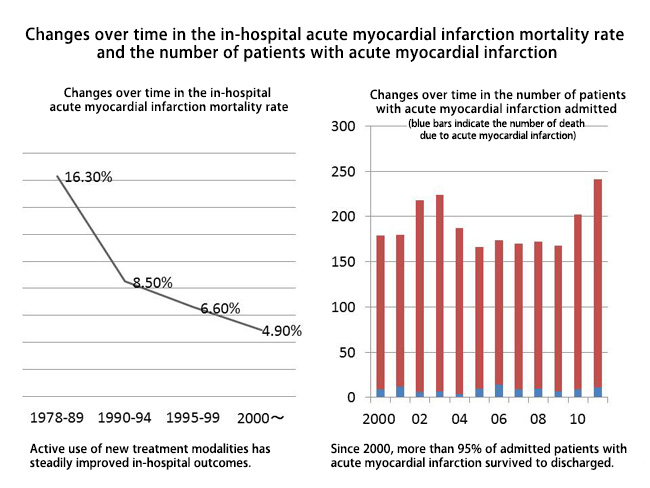
Following its inception, the CCU markedly improved survival outcomes in patients with acute myocardial infarction through early detection and treatment of fatal arrhythmia and cardiac failure. In the 1990s, use of percutaneous catheter intervention to treat patients with acute myocardial infarction further improved in-hospital outcomes. During percutaneous catheter intervention, a catheter is used to aspire obstructive coronary thrombus and destroy atherosclerotic plaques in order to achieve revascularization.
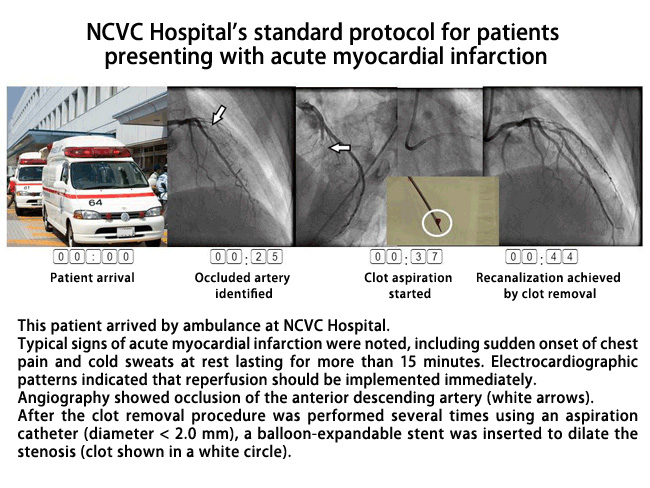
Clinical Applications of Imaging and Hemodynamic Analysis in Acute Myocardial Infarction
The pathogenesis of acute myocardial infarction includes atherosclerosis and other vascular abnormalities. In particular, plaque rupture has gained attention as the triggering event. Recent advances in imaging techniques have made it possible to detect such changes occurring in the body noninvasively.
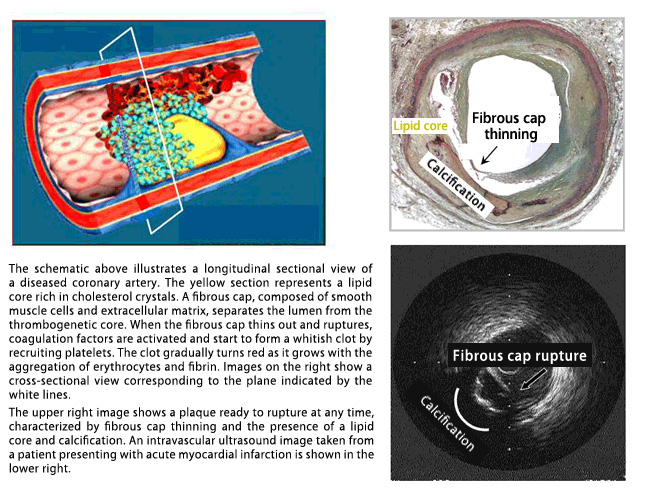
We use intravascular ultrasound, optical coherence tomography, and angioscopy to identify the cause and pathophysiology of cardiac disorders. Moreover, we measure fractional flow reserve in coronary arteries to evaluate the degree of blood flow reduction (ischemic burden).
last updated : 2021/10/01
