About NCVC
Researchers find the impact of hospital case volume on the outcomes after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation is ablation technology-dependent.
Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation (AF) has become a commonly performed procedure worldwide. The most critical problems in AF ablation are peri-procedural complications and the post-procedural recurrence of AF. A previous nationwide cohort study showed that a low hospital case volume (<50 or <100 procedures/year) was associated with adverse outcomes; however, there are few reports focusing on the case-volume effect according to the ablation technology.
A team of researchers, led by Dr. Yoshitaka Iwanaga, performed a nationwide cohort study using administrative data which covers almost all healthcare insurance in Japan and analyzed the effect of the annual case volume for atrial fibrillation catheter ablation on acute periprocedural complications and one-year success rate off antiarrhythmic drugs according to the ablation technology (radiofrequency ablation or cryoballoon ablation).
In the radiofrequency ablation group, acute complications and one-year AF recurrence decreased as the annual case volume increased to up to 150–200 cases/year. However, in the cryoballoon ablation group, these outcomes were similar regardless of the case volumes (Figure).
“The case-volume effect was noted in the radiofrequency ablation group, but not in the cryoballoon ablation group. Our results may affect the selection of ablation technology, especially in smaller case-volume hospitals and suggest that more experience is needed for safe and effective radiofrequency ablation when compared to cryoballoon ablation.” – Dr. Koshiro Kanaoka.
Next steps for this research are to clarify what strategies are recommended for hospitals with lower case volume or high-risk patients.
“This study provides an important suggestion for the selection of ablation technologies, especially in lower case-volume hospitals.” – Dr. Koshiro Kanaoka.
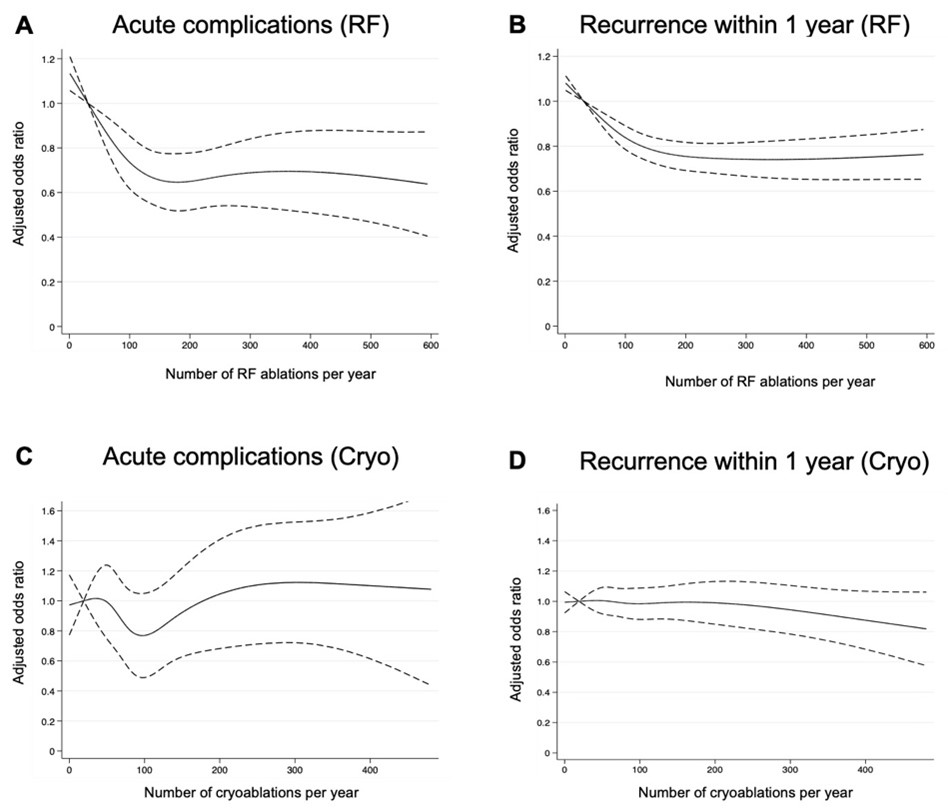
Figure. Case-volume effects according to ablation technology: radiofrequency ablation (A and B) and cryoballoon ablation (C and D).
last updated:2022/05/02
